create_self_signed_cert
This script will create a private key key.pem and a self-signed certificate cert.pem.
The following parameters are optional:
c-
the common name (
localhostif not given) of the certificate d-
the directory (
$PWDif not given) the key and certificate will be created in; will be created if it does not exit v-
the lifetime of the certificate in days (range: [1, 24855];
30if not given)Certificates with a lifetime exceeding 180 days will not be accepted by the Apple platform or Safari.
As of March 15, 2029, the maximum lifetime for a certificate will be 47 days.
x-
do not exit with an error if the key and certificate already exist
On macOS, the certificate will be added to the "login" keychain also.
|
The certificate created by this script is useful if
|
|
Chrome and Safari need no further configuration—you should restart your browser though. For Firefox, the created certificate has to be accepted manually. Docker needs to be restarted. |
|
Ensure that the common name ( /etc/hosts
⇓ /etc/hosts
|
|
Both If the given directory is inside a Git working tree, the script will offer to modify the .gitignore file: Related Script: git-cleanup |
|
Copy this script (and its related delete, renew, and verify scripts) into your Node.js project and add it as a custom script to your package.json
|
Usage
$ scripts/cert/create_self_signed_cert.sh
Adding 'localhost' certificate (expires on: 2024-02-29) to keychain /Users/example/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db ...
$ date -Idate
2024-01-30
$ stat -f '%A %N' *.pem
600 cert.pem
600 key.pem
$ openssl x509 -ext subjectAltName -noout -in cert.pem
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:localhost
$ openssl x509 -startdate -noout -in cert.pem
notBefore=Jan 30 16:25:43 2024 GMT
$ openssl x509 -enddate -noout -in cert.pem
notAfter=Feb 29 16:25:43 2024 GMT
$ scripts/cert/create_self_signed_cert.sh -d dist/etc/nginx
Adding 'localhost' certificate (expires on: 2024-02-29) to keychain /Users/example/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db ...
$ scripts/cert/create_self_signed_cert.sh -d dist/etc/nginx -x
$ scripts/cert/create_self_signed_cert.sh -d . -v 10
Adding 'localhost' certificate (expires on: 2024-02-09) to keychain /Users/example/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db ...
$ scripts/cert/create_self_signed_cert.sh -d ~/.local/secrets/certs/https.internal -v 20 -c https.internal
Adding 'https.internal' certificate (expires on: 2024-02-19) to keychain /Users/example/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db ...macOS
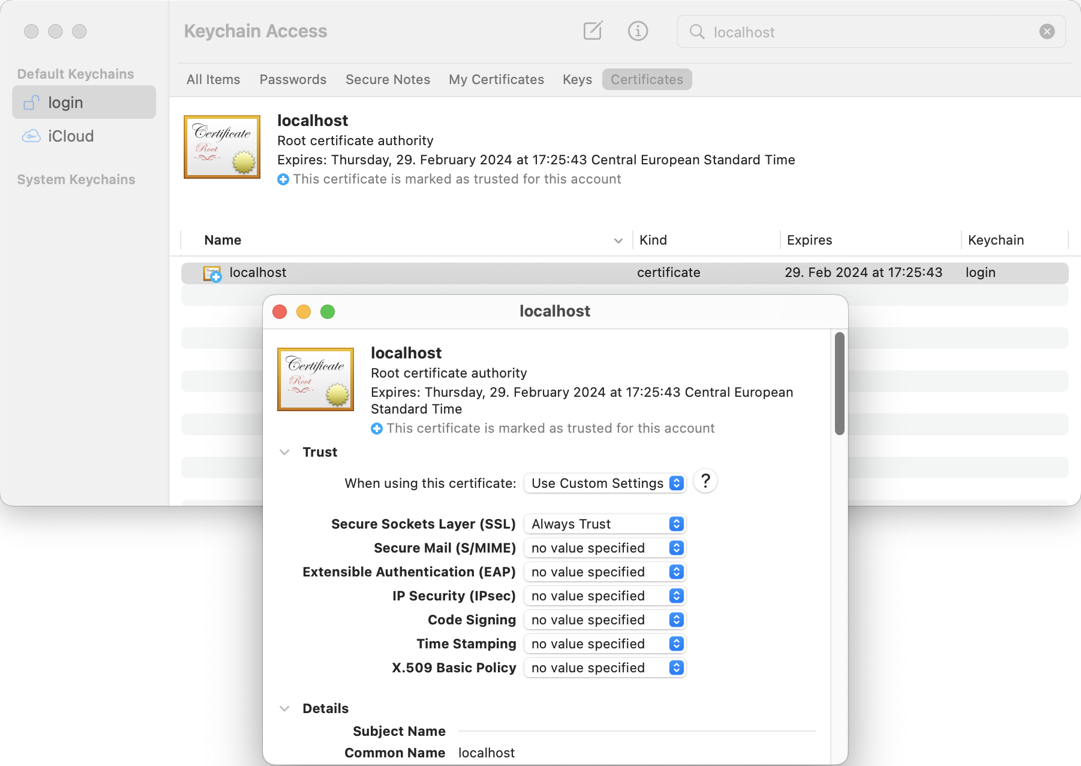
Check your "login" keychain in Keychain Access; Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) should be set to "Always Trust":
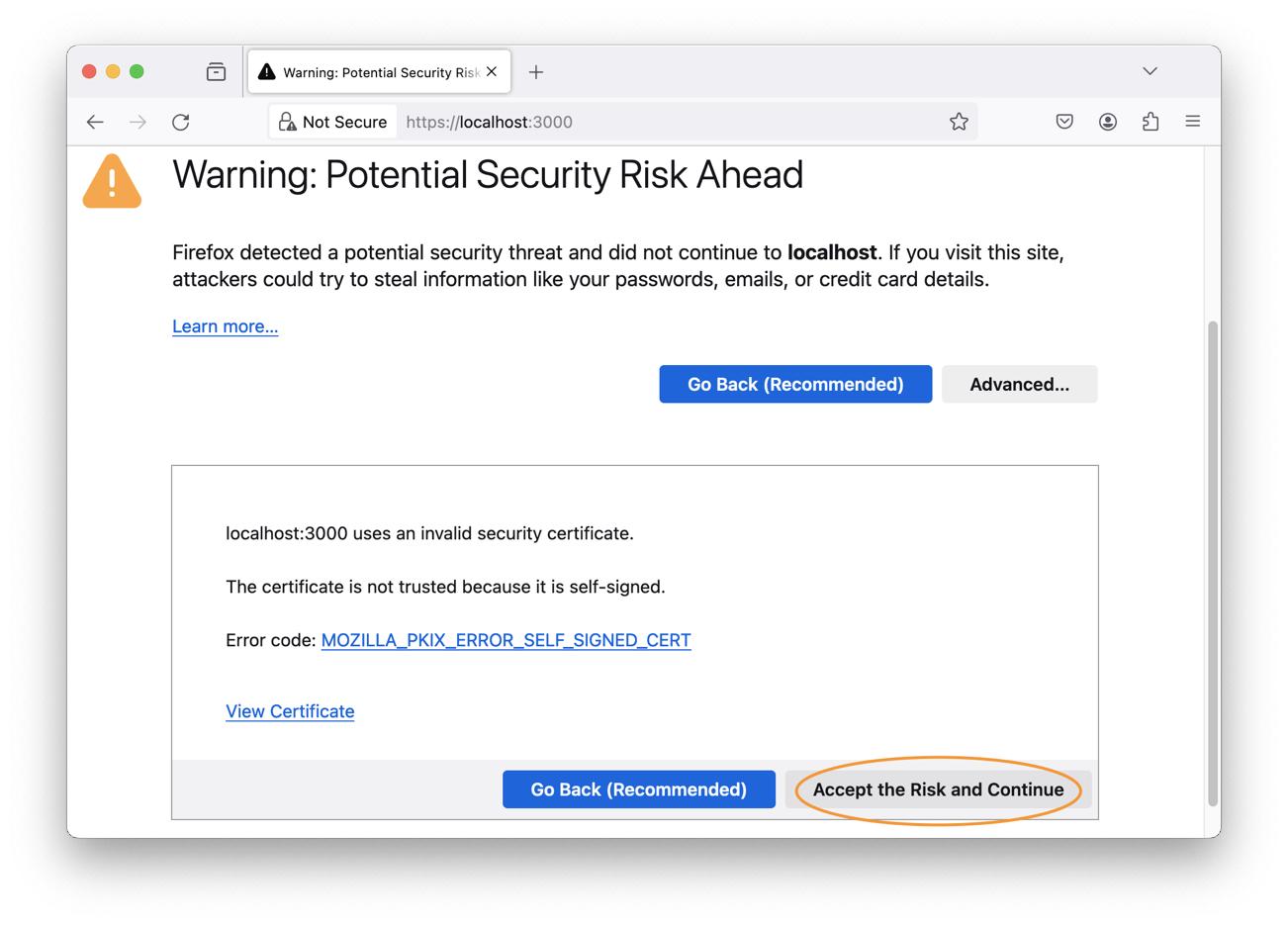
Firefox (MOZILLA_PKIX_ERROR_SELF_SIGNED_CERT)
You need to bypass the self-signed certificate warning by clicking on "Advanced" and then "Accept the Risk and Continue":
Examples
Apache HTTP Server
$ scripts/cert/create_self_signed_cert.sh -d ~/.local/secrets/certs/localhost
$ docker run --rm httpd:2.4.66-alpine3.23 cat /usr/local/apache2/conf/httpd.conf >httpd.conf.orig
$ sed -e 's/^#\(Include .*httpd-ssl.conf\)/\1/' \
-e 's/^#\(LoadModule .*mod_ssl.so\)/\1/' \
-e 's/^#\(LoadModule .*mod_socache_shmcb.so\)/\1/' \
httpd.conf.orig >httpd.conf
$ mkdir -p htdocs
$ printf '<!doctype html><title>Test</title><h1>Test</h1>' >htdocs/index.html
$ docker run -i -t --rm -p 3000:443 \
-v "$PWD/htdocs:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs:ro" \
-v "$PWD/httpd.conf:/usr/local/apache2/conf/httpd.conf:ro" \
-v "$HOME/.local/secrets/certs/localhost/cert.pem:/usr/local/apache2/conf/server.crt:ro" \
-v "$HOME/.local/secrets/certs/localhost/key.pem:/usr/local/apache2/conf/server.key:ro" \
httpd:2.4.66-alpine3.23nginx
$ scripts/cert/create_self_signed_cert.sh -d ~/.local/secrets/certs/localhost
$ printf 'server {
listen 443 ssl;
listen [::]:443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/server.key;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
}
}' >nginx.conf
$ mkdir -p html
$ printf '<!doctype html><title>Test</title><h1>Test</h1>' >html/index.html
$ docker run -i -t --rm -p 3000:443 \
-v "$PWD/html:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro" \
-v "$PWD/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf:ro" \
-v "$HOME/.local/secrets/certs/localhost/cert.pem:/etc/ssl/certs/server.crt:ro" \
-v "$HOME/.local/secrets/certs/localhost/key.pem:/etc/ssl/private/server.key:ro" \
nginx:1.29.4-alpine3.23-slimGo
$ cd scripts/cert/go/stdlib
$ ../../create_self_signed_cert.sh
$ go run server.goJava
$ cd scripts/cert/java/stdlib
$ ../../create_self_signed_cert.sh
$ openssl pkcs12 -export -in cert.pem -inkey key.pem -out certificate.p12 -name localhost -password pass:changeit
$ keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore certificate.p12 -srcstoretype pkcs12 -srcstorepass changeit -destkeystore keystore.jks -deststorepass changeit
$ KEYSTORE_PATH=keystore.jks KEYSTORE_PASS=changeit java Server.javaSpring Boot
$ cd scripts/cert/java/spring-boot
$ ../../create_self_signed_cert.sh
$ ./gradlew bootRunQuarkus
|
Instead of using this script, you might want to use Quarkus' own certificate tooling. |
$ cd scripts/cert/java/quarkus
$ ../../create_self_signed_cert.sh
$ ./gradlew quarkusDev